Short-chain fatty acid butyrate is essential for preserving gut health and has been related to many health advantages, such as decreased inflammation and enhanced digestive health. Beneficial gut bacteria ferment fiber in the colon to produce butyrate, which serves as the primary energy source for colon cells. It is essential for preserving the integrity of the intestinal barrier. One natural method to raise butyrate levels in the body is to include butyrate foods high in butyrate in one’s diet. Whole grains, onions, bananas, and legumes are foods high in resistant starch that boost butyrate synthesis. Certain nutrients’ importance can help maintain a balanced gut flora, improving general health and well-being.
Highest Butyrate Foods
By directly regulating the formation of butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid necessary for immune system support and gut lining integrity, foods high in butyrate are critical for promoting a healthy gut environment. Among the most effective for increasing butyrate levels are resistant starch-rich foods, which resist digestion in the small intestine and instead undergo fermentation in the large intestine, producing butyrate as a byproduct. Examples include cooked and cooled potatoes, unripe bananas, legumes, and whole grains. Additionally, dietary fibers found in garlic, onions, and leeks, known as prebiotics, significantly contribute to butyrate production by feeding beneficial gut bacteria. Prioritizing these high butyrate foods can enhance gut health, reduce inflammation, and promote a balanced microbiome, offering profound benefits for overall well-being.

List Of Foods With Butyrate
Resistant Starch Foods
- Cooked and Cooled Potatoes
- Green Bananas
- Legumes (Beans, Lentils, Peas)
- Whole Grains (Barley, Oats, Brown Rice)
- Rice Pasta (cooled after cooking)
- Cashews
- Whole Wheat Flour
Prebiotic Foods
- Garlic
- Onions
- Leeks
- Chicory Root
- Dandelion Greens
- Jerusalem Artichoke
- Banana Flour
Fiber-Rich Vegetables
- Artichokes
- Asparagus
- Broccoli
- Brussels Sprouts
- Cabbage
- Carrots
Fruits
- Apples
- Bananas
- Pears
- Avocado
- Raspberries
Nuts and Seeds
- Almonds
- Chia Seeds
Fermented Foods
- Sauerkraut
- Kimchi
- Kefir
- Yogurt with Live Cultures
The foods listed above are among the best butyrate foods for promoting butyrate production due to their high content of resistant starch, prebiotics, and fiber. These components are essential for feeding the beneficial bacteria in the gut, which, through fermentation, produce butyrate—a vital short-chain fatty acid. Butyrate is important in maintaining gut health, supporting the intestinal barrier, and modulating the immune system, making these foods that increase butyrate production integral to a healthy diet.
We may collect a commission at no additional cost to you if you make a purchase through any of the affiliate links in this post.
Benefits Of A Healthy Butyrate And Butyrate Foods
Incorporating butyrate foods into your diet can yield myriad benefits, including improved gut health, enhanced insulin sensitivity, and reduced inflammation. Beyond supporting digestive well-being, butyrate also offers neuroprotective effects, improves sleep quality, and may help manage cardiovascular disease. This highlights the importance of butyrate in maintaining a balanced and healthy body.
Butyrate is fundamental for maintaining a robust gut environment. It nourishes the cells of the colon, enhancing the integrity of the intestinal barrier. This action is crucial for preventing conditions like leaky gut syndrome, where harmful substances can enter the bloodstream, potentially leading to inflammation and other health issues. By reinforcing the gut barrier, butyrate ensures the proper absorption of nutrients while keeping out pathogens and toxins.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Butyrate’s anti-inflammatory qualities are essential for reducing continuing inflammation, which is the primary cause of multiple illnesses such as ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Butyrate promotes a balanced, healthy condition in the body by lowering needless inflammation and controlling the immunological response. Since chronic inflammation is connected to a myriad of health problems outside of the digestive system, this management is critical for gut health and overall health.
Metabolic Health
Significant effects of butyrate on metabolic health include improved insulin sensitivity and blood sugar management. Those who have diabetes or metabolic syndrome may benefit the most from this, as butyrate helps to stabilize blood sugar levels, lowering the chance of spikes and crashes. Additionally, butyrate promotes effective glucose metabolism and increases insulin sensitivity, which helps with overall energy balance and weight management.
Immune System Support
Another essential advantage of butyrate is that it supports the immune system. It encourages the development of regulatory T cells necessary for preserving immunological tolerance and reducing autoimmune responses. This mechanism helps the body to distinguish between harmful invaders and its own cells, reducing the risk of autoimmune diseases and allergies. Promoting a balanced immune response, butyrate contributes to the body’s resilience against infections and diseases.
Relieve Gastrointestinal Conditions
Butyrate is helpful in reducing the symptoms of several gastrointestinal disorders, including Crohn’s disease and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). It helps to calm the digestive tract and lessen symptoms like bloating, irregular bowel movements, and stomach pain by fortifying the gut barrier and lowering inflammation. Its ability to nourish colon cells promotes tissue repair and overall gastrointestinal health by aiding in mending injured tissues.
Increase Insulin Sensitivity
Another critical effect of butyrate is that it increases insulin sensitivity. Butyrate assists in the effective glucose uptake from the bloodstream into the cells, essential for energy production and preserving appropriate blood sugar levels. It does this by enhancing the body’s reaction to insulin. Those who already have type 2 diabetes or are at risk for the disease may find this step especially helpful since it helps control blood sugar levels and reduces the potential complications from the disease.
Enhance Sleep
Butyrate may also improve the overall quality of sleep. By modifying the gut-brain axis, butyrate affects the production of neurotransmitters and hormones related to the sleep-wake cycle, like melatonin and serotonin. Thus, appropriate butyrate production and healthy gut flora can support improved sleep patterns, which can help treat insomnia and enhance sleep quality.
Treat Cardiovascular Disease
Butyrate has been linked to cardiovascular health by reducing inflammation, one of the key contributors to heart disease. Its anti-inflammatory effects can help lower blood pressure and reduce cholesterol levels, which are significant risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Furthermore, butyrate’s role in promoting insulin sensitivity and regulating metabolism can also contribute to heart health by preventing obesity and metabolic syndrome, further reducing the risk of heart disease.
By addressing gastrointestinal issues, enhancing insulin sensitivity, protecting the brain, improving sleep, and offering cardiovascular benefits, butyrate demonstrates its vast therapeutic potential. These benefits reinforce the importance of incorporating butyrate foods into a balanced diet to support various aspects of health and well-being.
How Much Butyrate Do I Need?
The specific amount of butyrate required for optimal health can vary based on individual factors such as age, diet, and gut microbiome composition, and there isn’t a one-size-fits-all recommendation for butyrate intake. For women, ensuring a diet rich in fiber from various sources is crucial in promoting butyrate production in the gut. According to general dietary guidelines, women should take roughly 25 grams of fiber daily. This fiber, especially types fermentable by gut bacteria—such as resistant starch and soluble fiber—can significantly enhance butyrate production.
Eating diverse high-fiber butyrate foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, can naturally support butyrate levels. While direct butyrate supplementation (#AD) is an option for some, focusing on a fiber-rich diet that supports gut microbiota to produce butyrate naturally is generally recommended for maintaining women’s health.
– Take Me To The Official ORA Organics Website Now! –
Maximizing Butyrate Absorption: Tips And Tricks
For optimal absorption of butyrate, it’s crucial to incorporate butyrate foods into your daily meals strategically:
- By including a variety of butyrate-rich foods in your diet, such as resistant starches from cooled potatoes and green bananas and fibrous vegetables like onions and garlic, you provide a consistent supply of substrates for your gut bacteria to ferment into butyrate.
- Pairing butyrate-rich foods with healthy fats can boost butyrate absorption in the intestines. Fats act as facilitators, aiding the passage of butyrate from the gut lining into the bloodstream.
- Maintaining overall gut health through regular consumption of probiotic and prebiotic foods supports a healthy microbiome and further optimizes the production and absorption of butyrate.
By following these tips and tricks, you can effectively increase your butyrate levels, leveraging these foods’ full spectrum of health benefits.
Downsides And Side Effects Of Butyrate
As with any supplement, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare provider before starting butyrate supplementation to ensure it’s appropriate for your health needs and circumstances.
While butyrate is generally considered beneficial for health, especially regarding gut health and metabolic functions, there can be potential downsides and side effects, particularly regarding supplementation. Excessive butyrate supplementation, beyond what the body naturally produces from dietary fiber, might lead to digestive discomfort, including bloating, gas, or diarrhea in some individuals. This is because a sudden increase in butyrate can alter gut flora balance and intestinal conditions more rapidly than the digestive system can adapt. Moreover, individuals with a sensitivity to components in butyrate supplements, such as certain fillers or additives, may experience allergic reactions or other side effects.
While butyrate has anti-inflammatory properties, relying solely on supplements without addressing underlying dietary or lifestyle factors that contribute to gut health issues might not be effective in the long term.
An Example Diet Plan Focused On Optimizing Butyrate
Creating a diet plan focused on optimizing butyrate production involves incorporating a variety of fiber-rich and prebiotic foods (butyrate foods) to support gut health. Here’s a sample weekly diet plan that includes foods known to boost butyrate levels. Remember, the goal is to consume about 25 grams of fiber per day for women, as part of a balanced diet that encourages the natural production of butyrate in the gut.
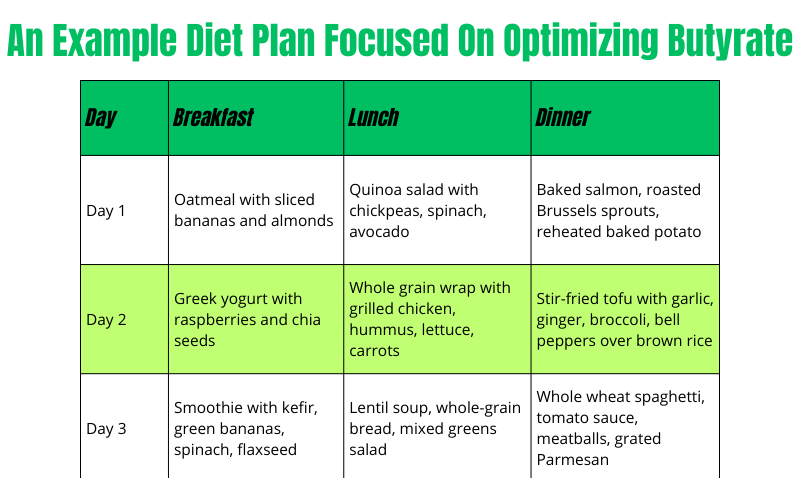
DOWNLOAD THE FULL PLAN DOWN HERE
Combining Butyrate Foods With An Exercise Plan
Combining butyrate foods with a comprehensive exercise plan can amplify the health benefits, synergizing overall well-being. Exercise can further increase the effectiveness of butyrate production from dietary fibers included in butyrate meals. Exercise is well known for improving gut health by increasing the variety of the gut microbiota. Frequent physical activity improves how much energy you use and lowers inflammation because it boosts metabolism and strengthens the gut’s capacity to ferment dietary fibers into butyrate.
Examples of this exercise include aerobics, strength training, and flexibility sessions. This holistic approach, integrating butyrate-rich foods with a balanced exercise regimen, supports optimal digestive health, reinforces the immune system, and contributes to better mental health outcomes, illustrating the interconnectedness of diet, exercise, and gut health.
FAQ
How can I increase my butyrate in my diet?
You can increase butyrate in your diet by consuming more fiber-rich and prebiotic foods, such as whole grains, legumes, green bananas, and vegetables like onions and garlic. You can download the one week diet plan for butyrate in this blog post as well!
What is the best form of butyrate?
The best form of butyrate is naturally produced in the gut through the fermentation of dietary fibers by beneficial bacteria.
Does Greek yogurt have butyrate?
Greek yogurt itself does not contain butyrate, but it can support the gut bacteria that produce butyrate through its probiotic content.
Conclusion
Butyrate is a cornerstone in pursuing optimal health, serving multiple pivotal functions within the body, from nurturing gut health and fortifying the immune system to its powerful anti-inflammatory properties. Its significance is underscored by its role in providing energy for colon cells, enhancing the integrity of the gut barrier, and regulating the body’s immune and inflammatory responses. The primary drivers of butyrate production include a diet rich in fiber and resistant starches—found abundantly in foods like legumes, unripe bananas, and fibrous vegetables such as onions and garlic—alongside maintaining a diverse and balanced gut microbiome.
Moreover, the synergy between butyrate-rich foods and a consistent exercise regimen amplifies butyrate’s beneficial effects. Physical activity boosts gut microbial diversity and enhances the gut’s capacity to convert dietary fibers into butyrate, illustrating the interconnectedness of diet, exercise, and gut health. Butyrate’s emerging roles in metabolic health, neuroprotection, sleep enhancement, and cardiovascular disease management highlight its broad therapeutic potential.

In conclusion, the importance of butyrate transcends gut health, impacting overall physiological well-being and disease prevention. Achieving optimal butyrate levels through a strategic combination of dietary choices and lifestyle practices offers a promising avenue for enhancing health outcomes. Therefore, embracing a lifestyle that promotes butyrate production—centered around a diverse, fiber-rich diet and regular physical activity—is integral for harnessing its full health benefits.












One thought on “Best Butyrate Foods 2024”